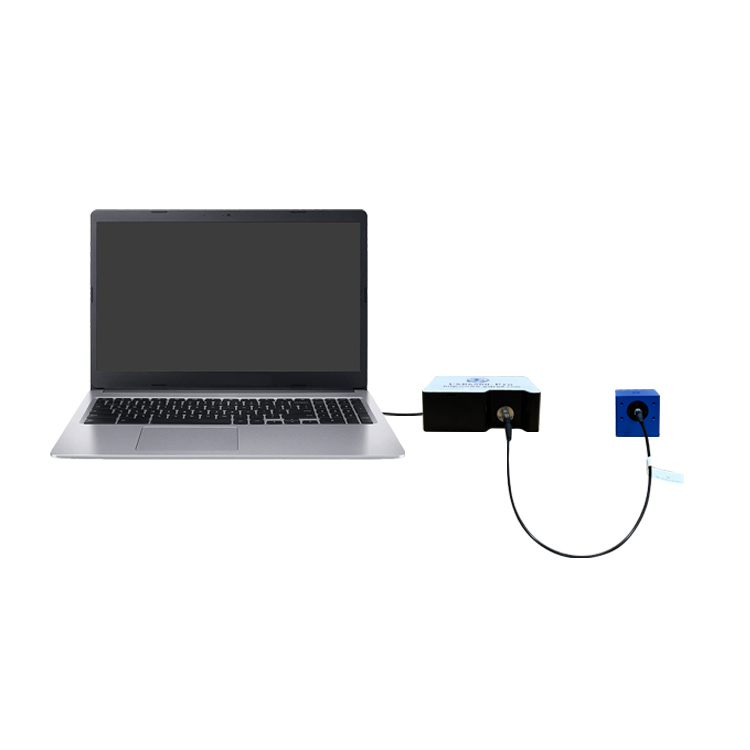
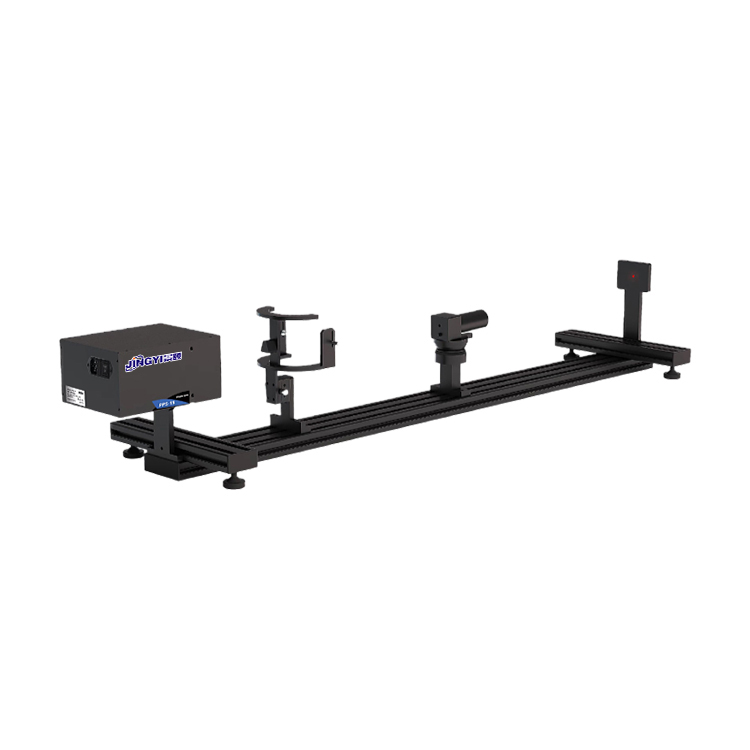
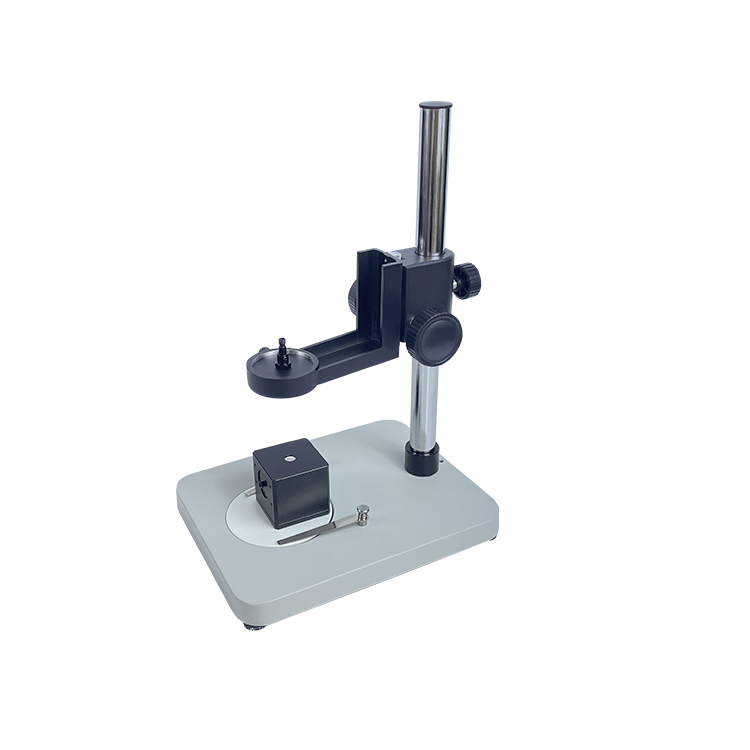
Integrating Sphere for Optical Detection Terminology & Application Manual
In the field of modern optical measurement, the integrating sphere for optical detection, as a critical optical instrument, has become increasingly important. It enables uniform scattering and diffusion of light, laying a reliable foundation for diverse optical measurements. Next, we will provide an in-depth discussion of the working principle, application scenarios, key purchasing considerations, and characteristics of different types of integrating spheres for optical detection.
Working Principle of Integrating Sphere for Optical Detection
The core structure of an integrating sphere for optical detection is a hollow spherical cavity coated with a specialized high-reflectance Lambertian coating. Owing to the properties of this coating, incident light is reflected with uniform intensity in all directions, allowing multiple reflections and scattering of light rays within the sphere. Following repeated reflections and scattering, light is distributed uniformly throughout the interior of the sphere, minimizing the influence of the original propagation direction of light rays. It preserves information such as color and intensity of light while discarding spatial distribution information.
From a physical perspective, the operating principle of integrating spheres for optical detection is based on the diffuse reflection and scattering of light. When light enters the interior of the integrating sphere, it is first reflected by the high-reflectance Lambertian coating. Due to the Lambertian characteristics of the coating, the intensity of reflected light is uniform across all directions. These reflected rays propagate further within the sphere and interact with one another, enhancing light scattering and mixing. After multiple rounds of reflection and scattering, a homogeneous optical field forms inside the sphere, achieving the homogenization of incident light.
Application Scenarios of Integrating Sphere for Optical Detection
Integrating spheres for optical detection are widely applied across numerous fields. Below are several common application scenarios:
Optical Power Measurement
Integrating spheres for optical detection can be employed to measure the optical power of lighting sources, lasers, light-emitting diodes (LEDs), and other light-emitting devices. By placing the light source under test inside the integrating sphere, the device collects all light emitted by the source and distributes it uniformly within the cavity. A detector then measures the light intensity inside the sphere, from which the optical power of the source can be calculated.
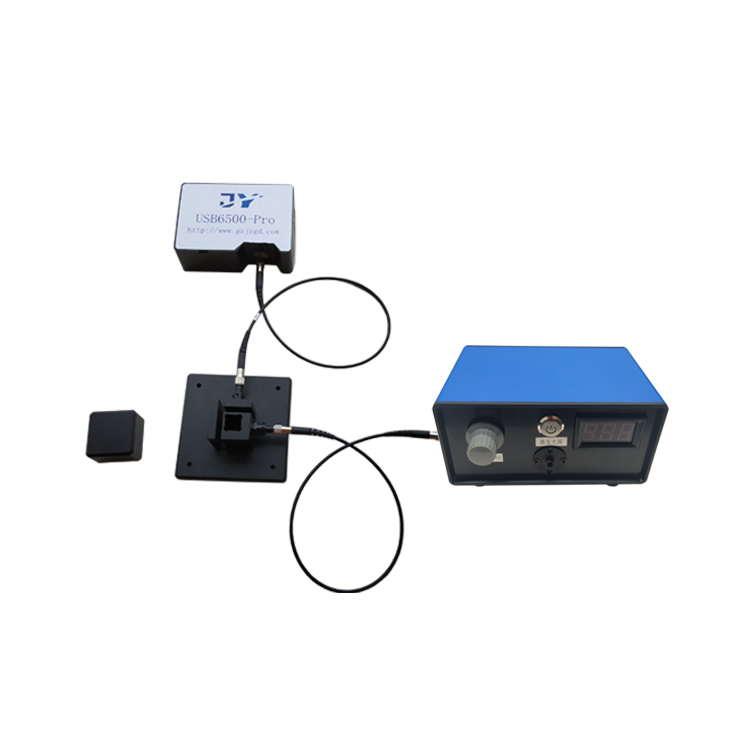
Spectral Measurement
Integrating spheres for optical detection can be used in conjunction with spectrometers to characterize the spectral distribution of light sources. In spectral measurements, the integrating sphere delivers homogenized light to the entrance slit of the spectrometer, improving the accuracy and resolution of spectral measurements.
Reflectance and Transmittance Measurement
Integrating spheres for optical detection are applicable for measuring the reflectance and transmittance of samples. With a sample positioned inside the integrating sphere, the intensity of light reflected or transmitted by the sample is measured, allowing the computation of the sample’s reflectance or transmittance.
Uniform Light Source
Integrating spheres for optical detection can serve as uniform light sources for calibrating other optical instruments or providing homogeneous illumination. By installing a light source inside the integrating sphere and adjusting parameters such as port size and internal coating, a uniformly distributed output optical field can be obtained.
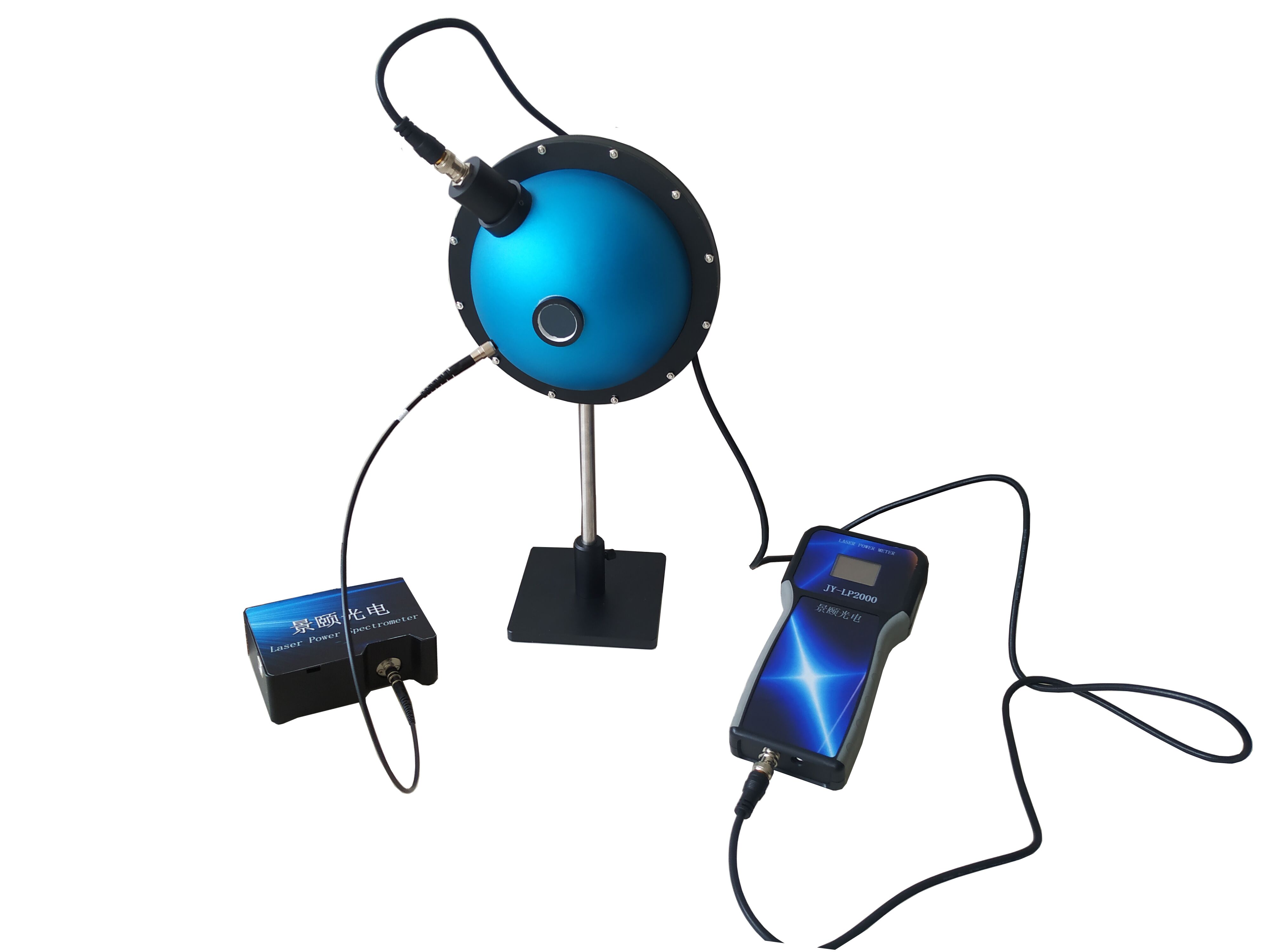
Laser Power Measurement
Integrating spheres are commonly used instruments for measuring high-power lasers. They disperse high-power laser radiation uniformly throughout the spherical cavity, preventing detector damage caused by excessive optical intensity. Meanwhile, the attenuation characteristics of integrating spheres contribute to more accurate and reliable measurement results.
Key Purchasing Considerations for Integrating Spheres for Optical Detection
Multiple factors must be evaluated when selecting an integrating sphere for optical detection to ensure it matches specific application requirements. The following are core purchasing guidelines:
Size Selection
The dimensions of an integrating sphere for optical detection are determined by practical application demands. Smaller integrating spheres are typically chosen for compact light sources or integration into other systems, while larger models are required for high-power sources or applications demanding a large, homogeneous output optical field. Generally, inner diameters of integrating spheres range from 1 mm to 3 m.
Internal Coating Selection
The internal coating is one of the key factors determining the performance of an integrating sphere. Higher reflectance of the diffuse coating correlates with improved light-collection efficiency and measurement precision. Coating materials should be selected based on application requirements and operating spectral bands.
· For deep-ultraviolet, extreme physics, and vacuum applications, sintered polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE/Teflon) coatings are typically preferred.
· For visible-band applications, white diffuse coatings are commonly adopted.
· For near-infrared to mid-infrared (NIR–MIR) bands, gold-plated diffuse reflective coatings are routinely used.
Configuration Selection
Configurations of integrating spheres include the number of ports, number of detector ports, and inclusion of internal baffles, among other parameters. These specifications affect measurement accuracy and application scope and should be determined according to practical needs.For instance, integrating spheres with multiple ports are suitable for devices emitting in multiple directions. For highly divergent laser diodes, removing baffles and positioning the detector close to the entrance port can eliminate initial optical hotspots, minimizing the risk of saturation or damage to photodiodes.
Sensitivity and Accuracy
Sensitivity and accuracy are critical performance indicators for integrating spheres. When selecting a model, verify whether these metrics satisfy application requirements. In general, integrating spheres exhibit slightly lower sensitivity compared with traditional power meters, yet rational design and calibration can enhance measurement accuracy and reliability.
Brand and Quality
As high-precision optical instruments, the quality and performance of integrating spheres directly determine the validity and dependability of measurement results. It is recommended to select reputable brands with robust quality assurance and after-sales technical support.
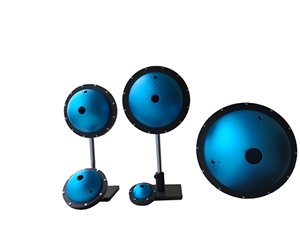
Characteristics of Different Types of Integrating Spheres for Optical Detection
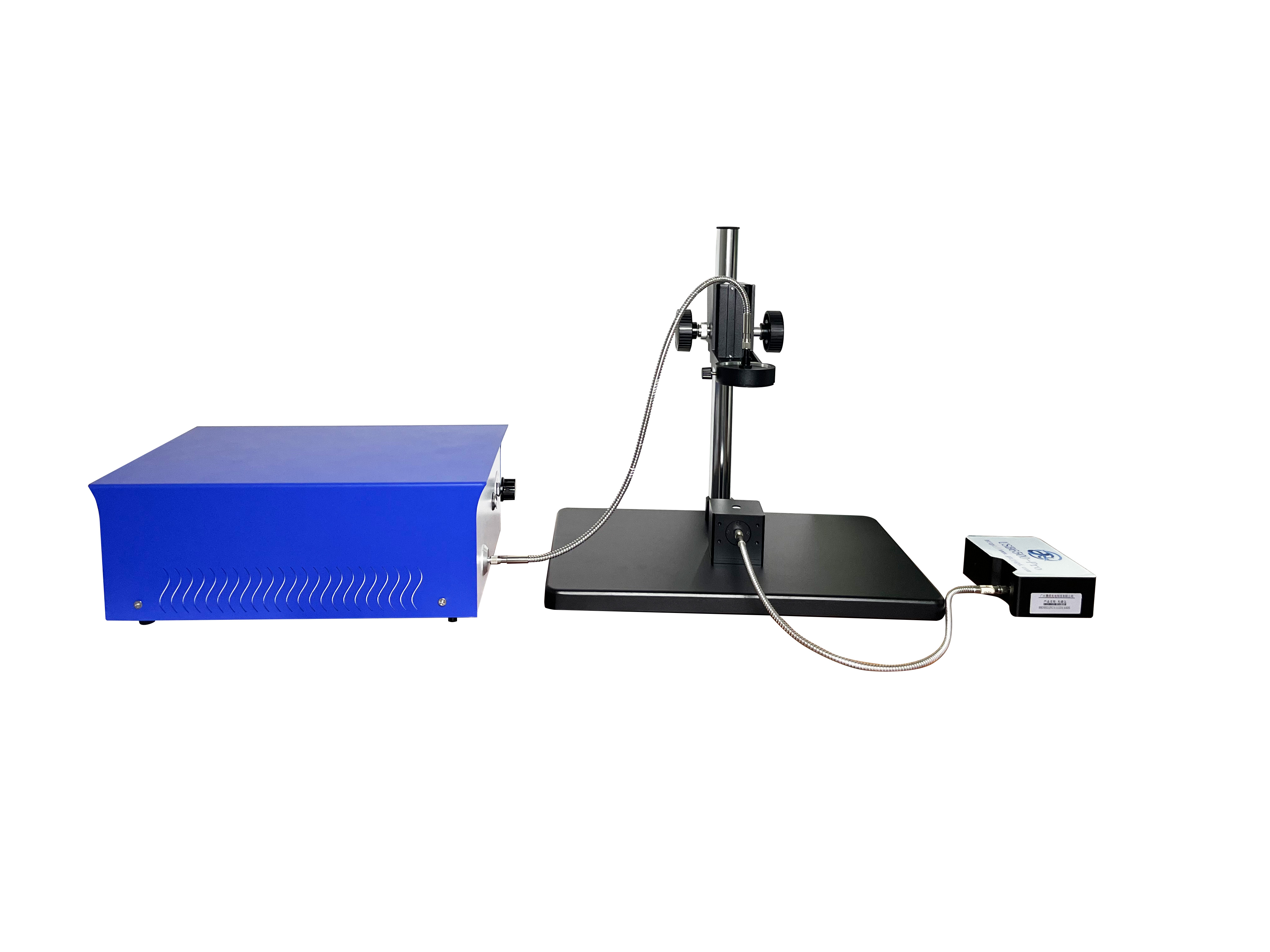
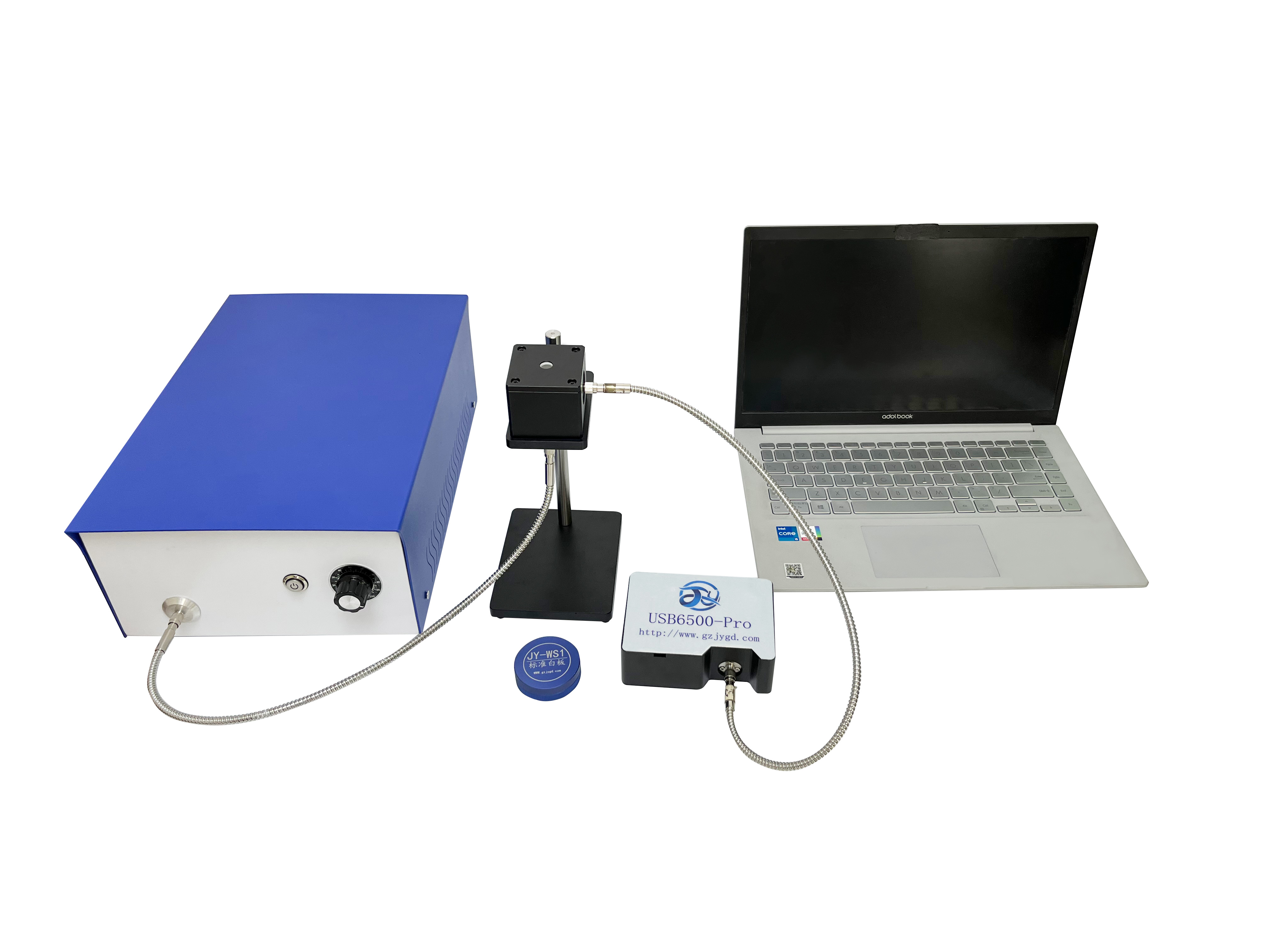
General-Purpose Integrating Spheres for Optical Detection
General-purpose integrating spheres are compatible with various spectral measurement systems, offering high cost-performance and versatility. As an example, the JY-FOIS84 general-spectrum integrating sphere from Jingyi Optoelectronics features universal ports, allowing rapid installation of matching accessories for different applications to fulfill multi-purpose usage with simple operation and flexible deployment. It employs diffuse coating with high stability, ideal Lambertian behavior, and excellent diffuse reflectance, resisting yellowing and peeling to deliver superior testing performance.
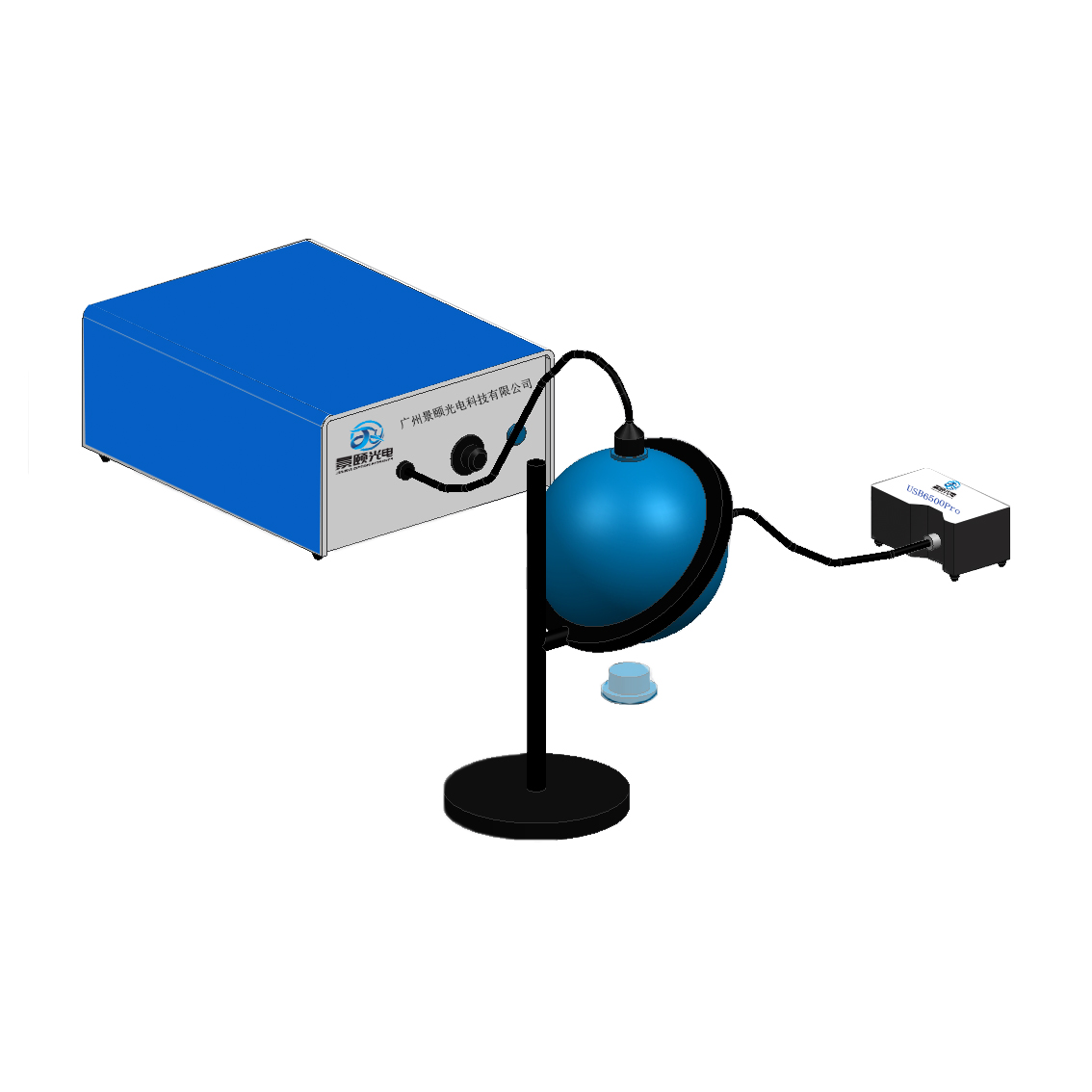
Uniform Light Source Integrating Spheres
Uniform light source integrating spheres are primarily designed to generate homogeneous output optical fields, used for calibrating other optical instruments or providing uniform illumination. These models usually feature large dimensions and high reflectance coatings to achieve spatially uniform light distribution.
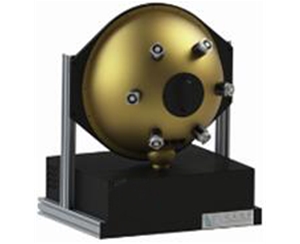
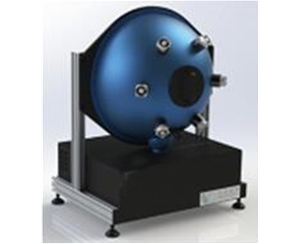
Laser Power Integrating Spheres
Laser power integrating spheres are specialized for measuring high-power laser radiation. They typically feature large sizes and strong attenuation properties, uniformly distributing high-intensity laser light within the cavity to protect detectors from optical damage.
Reflectance and Transmittance Integrating Spheres
Reflectance and transmittance integrating spheres are dedicated to characterizing the reflective and transmissive properties of samples. They often incorporate specialized designs to accurately measure the intensity of light reflected or transmitted by samples, enabling precise calculation of reflectance and transmittance values.
Jingyi Optoelectronics maintains a high factory pass rate, with products featuring high-average-reflectance PTFE coatings, customizable dimensions and interfaces, and comprehensive pre-sales and after-sales technical support.
Applicable scenarios: High-precision optical metrology including LED luminous flux testing, laser power measurement, display color correction, environmental monitoring, etc.
In summary, as an essential optical instrument, the integrating sphere for optical detection plays a pivotal role in modern optical metrology. When selecting an integrating sphere, factors including size, internal coating, configuration, sensitivity, and accuracy must be comprehensively evaluated based on practical application requirements. Additionally, priority should be given to reputable brands with reliable quality assurance and after-sales services. Proper selection and application of integrating spheres enhance the accuracy and reliability of optical measurements, providing robust support for scientific research, manufacturing, and industrial applications.
#OpticalDetectionIntegratingSphere #IntegratingSphere #TransmittanceIntegratingSphere #LightTransmissionIntegratingSphere #CoatedIntegratingSphere #UniformLightSourceIntegratingSphere